Things to know about cystinuria
Cystinuria is a rare disease that causes amino acid cystine stones in the bladder, kidneys, and ureters. This disease is inherited and is often passed down to children from their parents due to the defect in their genes. Cystinuria is inherited by a child from both their parents, not just one. This condition leads to the accumulation of cystine inside the kidneys and affects the functioning of the kidneys.
People who suffer from this condition develop stones that are made of amino acid cysteine that get stuck in the ureters, kidneys, and bladder. This often causes a lot of pain till the stone passes out of the body through urination. However, in cases where the stones are too large to pass through, a surgical method for removal is required.
The problem with this disease is that the stones can recur amino acid cystine in the body. Therefore, there are treatments available to control the pain and prevent the formation of more stones.
Symptoms of cystinuria
Cystinuria is a lifelong condition that has symptoms that usually occur when a person reaches the young adult age. However, cases have been reported where the symptoms were present in infants and adolescents as well. The symptoms of cystinuria are mentioned below:
- Blood in urine
- Nausea and vomiting
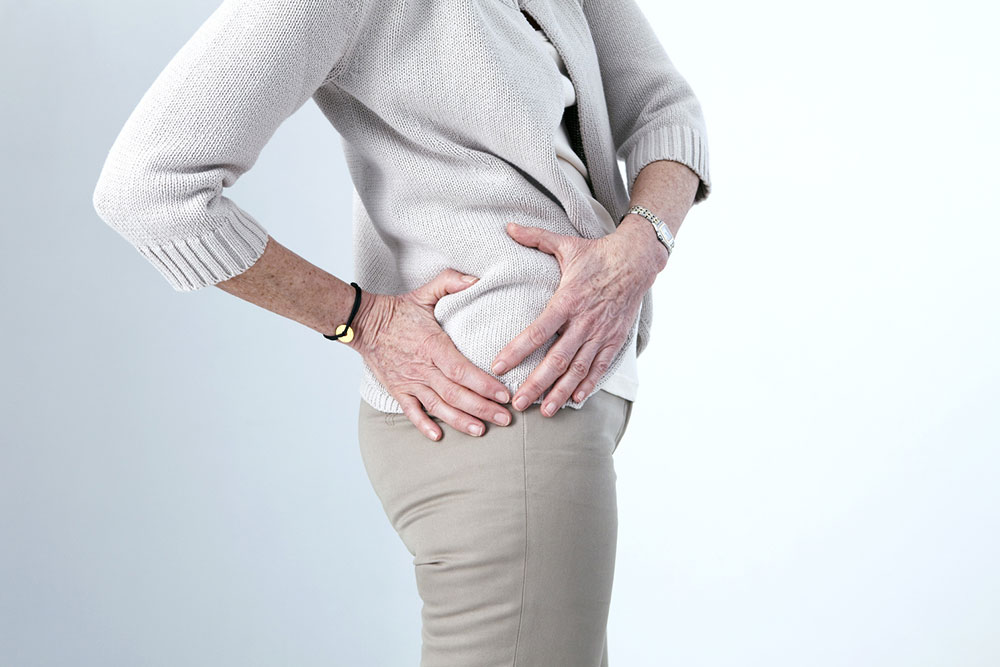
- Excruciating pain in the side or the back of the abdomen.
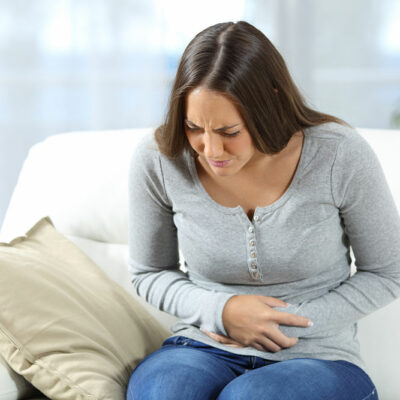
- Pain in the groin area, pelvis, or abdomen
These symptoms are experienced by patients only when there are stones present in the body. Therefore, this disease is called asymptomatic, which means there are no symptoms when the stones are not present. So, the pain or symptoms will occur every time the amino acid cystine forms new stones.
Cause of cystinuria
This condition is caused when there is a defect in the SLC3A1 and SLC7A9 genes. The purpose of these genes is to provide instructions for the body to produce transportation protein, which is found in the kidneys. This transportation protein controls the reabsorption of certain amino acids back into the bloodstream. Therefore, when the reabsorption does not happen due to a defect in the genes, the amino acids turn into kidney stones.
To understand the cause of cystinuria, it is important to learn about amino acids. Amino acids are formed from the digestion process when the body breaks down the proteins. These amino acids are important for several bodily functions and are not waste. Therefore, they are absorbed back into the bloodstream, which does not happen when there is a defect in the genes responsible for reabsorption.
A type of amino acid, called the cysteine, is not a very urine soluble acid; therefore, when it is not reabsorbed, it starts accumulating in the kidney, forming crystals or cystine stones.
Preventive measures
When both the parents of a child have defected genes, this disease cannot be prevented. However, by drinking plenty of water and reducing the intake of salt, along with taking the right medication, one can prevent the formation of kidney stones.